International Sugar Organization (ISO) released its third revision of the global 2024-25 sugar balance.
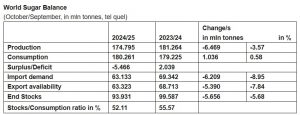
ISO’s fundamental view of the global supply/demand situation sees a large global deficit (the difference between forecast world consumption and production) of 5.466 million tonnes, up 0.585 million tonnes since February. A global deficit of this magnitude has not been seen for nine years. World production in 2024/25 was revised to 174.795 mln tonnes, down 6.469 mln tonnes from last season. Drivers include lower than expected production in India and Pakistan. World consumption is projected to reach a record 180.261 mln tonnes in 2024/25, down 0.160 mln tonnes on our previous estimate, while the 2023/24 estimate is revised to 179.225 mln tonnes, down 0.747 mln tonnes, on submissions from ISO members. These revisions result in forecast consumption growth of less than 0.6%.
According to the ISO, changes in trade dynamics are key market considerations. The estimated volume of trade in 2024/25 is anticipated to decline substantially, with exports falling to 63.323 mln tonnes from 69.342 mln tonnes last season, and yet, the trade balance is neutral as import demand totals 63.133 mln tonnes. Consequently, the global deficit is being offset by reductions in national stocks. While this might be a reason for the lack of price response to the increasing deficit, the global stock situation will end the season at a 9-year low.
The ending stocks/consumption ratio for 2024/25 is estimated to fall to 52.11%, from 55.57% at the end of 2023/24. As has been the norm over the last year, the ISO is also reporting an adjusted stock total figure, to reflect losses in the refining process as well as stock updates from members, which could reach a 13-season low in September.
ISO release stated that over the past three months, since the previous Quarterly Market Outlook, global sugar prices have weakened. The ISA Daily Price and the ISO White Sugar Price Index for the first 13 days of May averaged USD17.74 cents/lb and USD491.04/tonne, respectively. The outlook for prices over the next three months remains neutral-to-bullish as the deficit has widened, requiring CS Brazil producers to maintain uninterrupted operations to match or approach their May-September 2024 export levels.
Global ethanol production is forecast to reach 120.7 bln litres in 2025, rising 1.9% from 118.5 bln litres in 2024, with consumption projected to grow similarly to 119.5 bln litres. This expansion continues despite economic headwinds, underscoring the structural strength of renewable fuel mandates worldwide. Regional dynamics show important variations, with US production moderating to 60.7 bln litres, while Brazil’s output is expected to increase to 34.48 bln litres, supported by record corn-based ethanol production of 9.5 bln litres. India’s production shows the most dramatic growth trajectory, as it is projected to reach 8.0 bln litres in 2025 to support its ambitious 20% blending target, with a roadmap recently approved to reach 30% by 2030.
EU molasses prices are likely to trend higher during 2025 as local supplies are expected to fall in the face of a sharp reduction in the area sown to beet. More broadly, molasses prices are likely to be supported going forward by ongoing tight exportable supplies in 2025, as the number of countries exporting to the world market remains limited, in the context of India’s ongoing tax on molasses exports and voluntary sanctions against Russian product. Both the EU and US imported less in 2024, but for 2025 the EU’s higher molasses deficit is anticipated to see gains in import volumes later in the year. In the US, ongoing competitive corn prices, for feed inclusion, and imposition of a 10% import tax will see imported molasses volumes shrink.
As per ISO, in the world of high intensity sweeteners, acesulfame-K has been declared safe by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) following a re-evaluation process. However, there are mounting concerns over the safety of aspartame, with growing calls to ban it. Cargill’s fermentation-based stevia sweetener has been approved in the EU. New research attributes antimicrobial properties to saccharin but show that sucralose may be contributing to the global obesity levels through its impacts on the human brain.
















